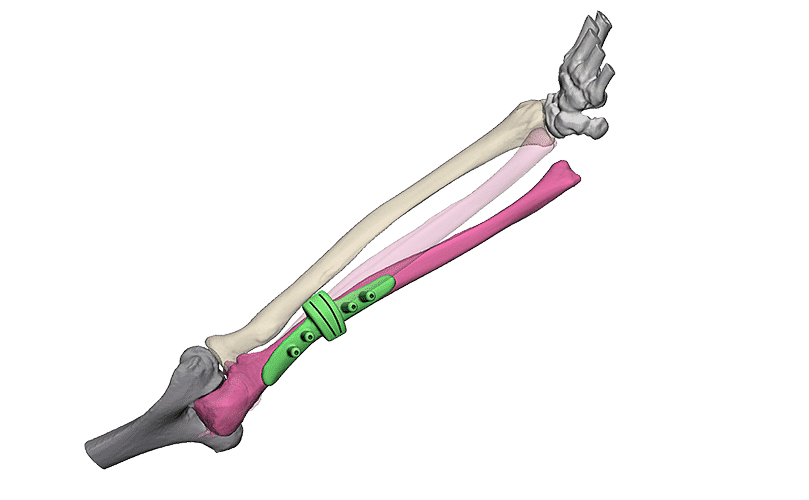
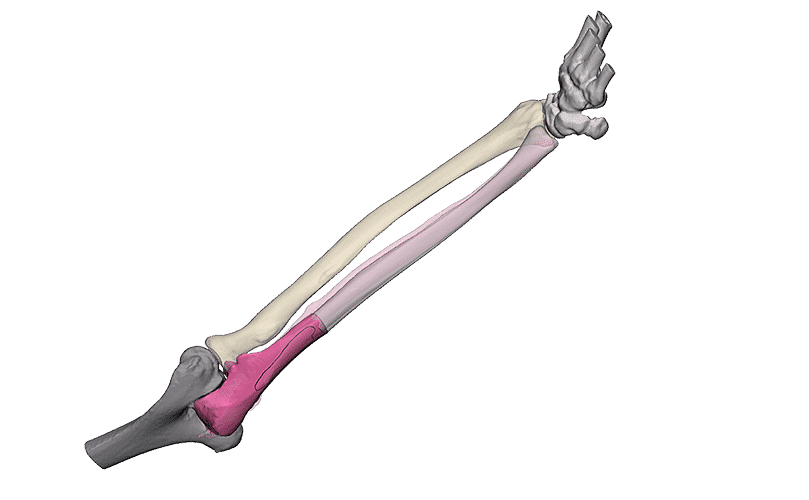
Fracture reduction
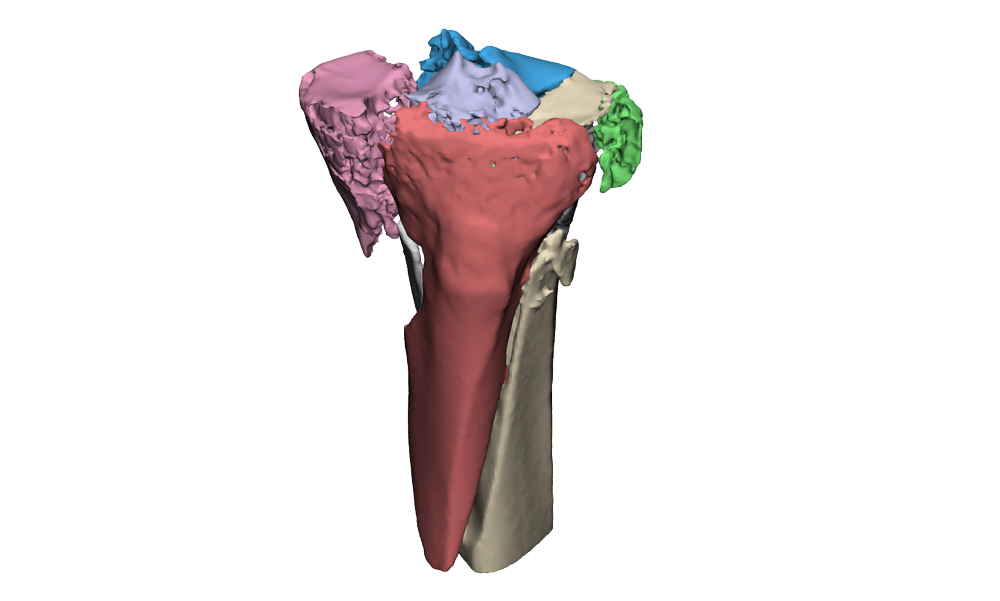
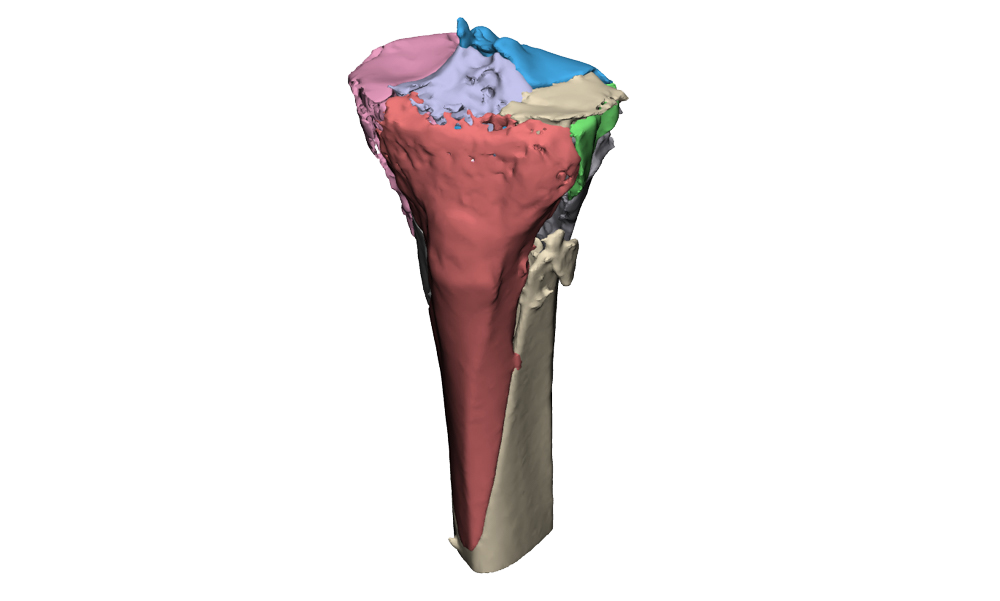
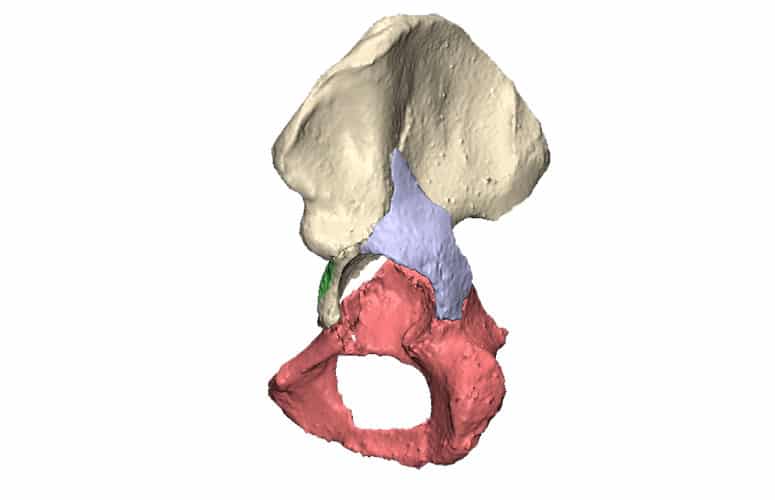
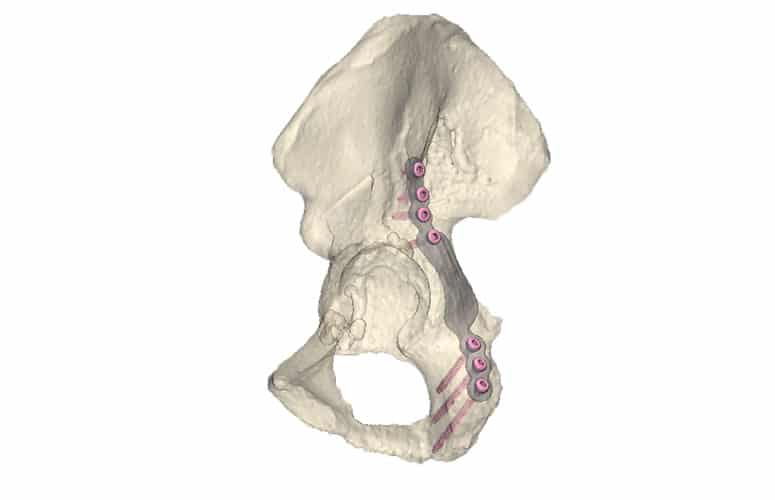
Intra-articular fractures are complex injuries with fracture lines in multiple directions. The fracture fragments are often displaced and rotated in different directions, which makes it complicated to get a complete picture of the injury with the current imaging. A 3D model can aid in getting a better understanding of the extent of the injury. This not only gives insight in the pattern of the fracture lines, but also the injury can be viewed from all sides. Additionally, it is possible to virtually reduce the fracture, using the healthy contralateral side. This can aid in creating a treatment plan.
Warning: Array to string conversion in /customers/3/1/a/3dlabgroningen.nl/httpd.www/wp-content/plugins/twenty20/inc/elementor-class.php on line 150
Warning: Undefined array key "align" in /customers/3/1/a/3dlabgroningen.nl/httpd.www/wp-content/plugins/twenty20/inc/elementor-class.php on line 151